Before we talk about the ways to earn cryptocurrency online, or leverage crypto to obtain more fiat stores of value or even goods and services, we need to talk about where the crypto that we wish to obtain is going to go. Because of the inherent flexibility of storing encryption keys in an encrypted format, there are multiple options available, each with its own upsides and downsides as regards security and ease of trading.
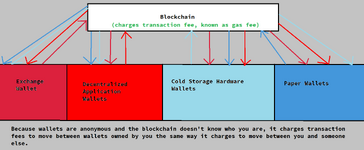
Given the fact that cryptocurrencies are groups of hashed numbers whose transactions are stored on encrypted blockchains with hashed wallet addresses, and that these wallets are also encrypted, one may expect cryptocurrency to be one of the most secure payment methods available. To a large extent, this is true. However, crypto currency hasn't factored in one of the biggest problems with security: human error and human ownership. This means that wallet types are distinguished not only by what functions they allow you to perform, but also how secure they are.
One of the main security factors is the private keys that the wallet owner possesses. Private keys are also used to verify the ownership of a part of the crypto blockchain for each wallet, and are used to sign transactions. Who owns the private keys and who can access them are key points of failure in cryptocurrency security. (The other key point of failure is that crypto transactions are immutable, meaning that if you get the wallet address even one letter incorrect, that transaction will be sent to someone other than whom you intended to send it to, and the crypto is gone forever unless the lucky recipient kindly chooses to send it back via another transaction. But this can happen with any wallet.)
The practice of sending crypto purchased through an exchange into a decentralized wallet or a hardware wallet is recommended, however, because an exchange wallet owns the private keys of all of its customers out of necessity. The only thing that connects your crypto to you on an exchange is your username and password. If the exchange goes down like FTX or becomes illegal in your country or you run afoul of the exchange's terms of service, you could lose the entire value of your investment. The latter two possibilities haven't resulted in users losing funds yet, but who knows what the future may bring.
Despite the risks, exchanges and exchange wallets have their advantages, because they allow you to buy and sell crypto the way someone might sell or buy a stock. For example, on Coinbase you can set up LIMIT orders where you can buy a cryptocurrency when it reaches a certain low price, and sell when the price of your chosen cryptocurrency reaches a certain a high price. Because crypto prices can change very rapidly, this will attempt to ensure that you buy or sell your crypto at the price you want. They also allow for staking, a way to contribute your crypto toward Proof of Stake for cryptocurrencies that operate that way (mostly Ethereum and derivative tokens), which can earn you a small amount of crypto over time by voting in contribution to cryptocurrency projects.
Basically exchanges are like the crypto equivalent of Robin Hood, and staking is like investing in dividend stocks. There are some differences, but the ideas are kind of the same. The main difference is that you are backing a decentralized currency instead of a company.
However, the crypto space gets even weirder, because there are decentralized exchanges like UniSwap that buy and sell crypto via peer-to-peer transactions, using liquidity pools and arbitrage to set prices that match the other, more custodial exchanges like Coinbase. Meanwhile, Coinbase Wallet is not the same as the Coinbase exchange - it's a decentralized hot wallet like Metamask that is controlled via a browser extension and supports more coins, including Bitcoin. (Are you confused yet?) Always read the fine print and look up several pieces of information before deciding to go with a crypto exchange or wallet to make sure you know what you're dealing with.
Since decentralized wallets allow users to hold onto their own private keys, they are more secure than an exchange. However, the downside of these hot wallets is that they are connected to the Internet, and these applications have your wallet address and private keys in them in order to facilitate Internet transactions. If your computer is hacked into, the hackers could send all of your crypto in that wallet to them and you would have no way to get it back.
Basically these wallets are like the way Paypal works for fiat currency. It is secure as long as you guard your private key and device from hackers, the same way you must guard your Paypal address and password, and all devices that save it automatically, like your phone.

Because of how these wallets work, it is advised to set them up with a computer that is disconnected from the Internet and to buy the wallet directly from the device manufacturer to avoid being defrauded out of your money on device setup. This is not something you should buy used. In addition, your crypto is only as secure as your access to your cold wallet device.
Finally, since all cryptocurrency is stored on the blockchain, your cold wallet only holds your public and private keys. In order to transfer your funds from one cold storage wallet to another you still need to pay a transaction fee to update the blockchain with the new wallet address. It is theoretically possible to transfer funds from one cold wallet to another, but in order to do so you still need to access the blockchain network which can open the users up to security risks. This is why cold storage hardware wallets are used for storage and not for frequent transactions - the less contact the wallet has with the Internet, the safer it is.
These wallets are the equivalent of a bank account or bank vault. They are secure until their information is exposed and the fraudsters can rack up fraudulent transactions.
Basically, these wallets are the crypto equivalent of cash. It is advised to store these papers in a secure safe or safe deposit box and import them into a cold storage hardware wallet at the soonest possible opportunity, in much the same way that you should not be hoarding cash under your mattress and instead deposit that cash into your bank account.
If you manage to gain a lot of crypto, investing in a cold storage wallet may be a good choice. Just keep in mind that every time you exchange your crypto from one wallet to another, you will pay transaction fees which vary based on the cryptocurrency that you're transferring in order to update the blockchain accordingly.
Given the fact that cryptocurrencies are groups of hashed numbers whose transactions are stored on encrypted blockchains with hashed wallet addresses, and that these wallets are also encrypted, one may expect cryptocurrency to be one of the most secure payment methods available. To a large extent, this is true. However, crypto currency hasn't factored in one of the biggest problems with security: human error and human ownership. This means that wallet types are distinguished not only by what functions they allow you to perform, but also how secure they are.
One of the main security factors is the private keys that the wallet owner possesses. Private keys are also used to verify the ownership of a part of the crypto blockchain for each wallet, and are used to sign transactions. Who owns the private keys and who can access them are key points of failure in cryptocurrency security. (The other key point of failure is that crypto transactions are immutable, meaning that if you get the wallet address even one letter incorrect, that transaction will be sent to someone other than whom you intended to send it to, and the crypto is gone forever unless the lucky recipient kindly chooses to send it back via another transaction. But this can happen with any wallet.)
Type 1: Exchange Wallets
Exchange wallets are primarily designed with the investment and trading aspects of cryptocurrency in mind. The most common ones are Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase, although more exist. They are primarily designed to function within the exchange that hosts them, however, the coins can be transferred to any other wallet type on this list via a transaction in which the exchange wallet address sends the coins to a different wallet address.The practice of sending crypto purchased through an exchange into a decentralized wallet or a hardware wallet is recommended, however, because an exchange wallet owns the private keys of all of its customers out of necessity. The only thing that connects your crypto to you on an exchange is your username and password. If the exchange goes down like FTX or becomes illegal in your country or you run afoul of the exchange's terms of service, you could lose the entire value of your investment. The latter two possibilities haven't resulted in users losing funds yet, but who knows what the future may bring.
Despite the risks, exchanges and exchange wallets have their advantages, because they allow you to buy and sell crypto the way someone might sell or buy a stock. For example, on Coinbase you can set up LIMIT orders where you can buy a cryptocurrency when it reaches a certain low price, and sell when the price of your chosen cryptocurrency reaches a certain a high price. Because crypto prices can change very rapidly, this will attempt to ensure that you buy or sell your crypto at the price you want. They also allow for staking, a way to contribute your crypto toward Proof of Stake for cryptocurrencies that operate that way (mostly Ethereum and derivative tokens), which can earn you a small amount of crypto over time by voting in contribution to cryptocurrency projects.
Basically exchanges are like the crypto equivalent of Robin Hood, and staking is like investing in dividend stocks. There are some differences, but the ideas are kind of the same. The main difference is that you are backing a decentralized currency instead of a company.
Type 2: Decentralized Application Wallets (Hot Wallets)
The second type of wallet is for people who want to interact with Web3 applications and send cryptocurrencies through the Internet to their friends or business partners. If you're looking for a wallet to interface with faucets, airdrops, and play crypto games, this type of wallet is for you. You'll also want this kind of wallet to engage in DeFi or purchase an NFT. The most common wallets of this type are Trust Wallet and Metamask. Electrum is a common decentralized Bitcoin wallet, while Metamask only holds Etherum and ERC-20 tokens.However, the crypto space gets even weirder, because there are decentralized exchanges like UniSwap that buy and sell crypto via peer-to-peer transactions, using liquidity pools and arbitrage to set prices that match the other, more custodial exchanges like Coinbase. Meanwhile, Coinbase Wallet is not the same as the Coinbase exchange - it's a decentralized hot wallet like Metamask that is controlled via a browser extension and supports more coins, including Bitcoin. (Are you confused yet?) Always read the fine print and look up several pieces of information before deciding to go with a crypto exchange or wallet to make sure you know what you're dealing with.
Since decentralized wallets allow users to hold onto their own private keys, they are more secure than an exchange. However, the downside of these hot wallets is that they are connected to the Internet, and these applications have your wallet address and private keys in them in order to facilitate Internet transactions. If your computer is hacked into, the hackers could send all of your crypto in that wallet to them and you would have no way to get it back.
Basically these wallets are like the way Paypal works for fiat currency. It is secure as long as you guard your private key and device from hackers, the same way you must guard your Paypal address and password, and all devices that save it automatically, like your phone.
Type 3: Cold Storage Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets)
The third type of wallet is for people who want to save large amounts of crypto currency and related digital assets for a long period of time. This is the for the man or woman who buys $1 million dollars worth of bitcoin and wants to save it for his or her retirement. Because these hardware wallets aren't connected to the internet, they are safe to store cryptocurrencies in for long periods of time. The most common wallets of this type are Ledger, Keepkey, and Trezor.Because of how these wallets work, it is advised to set them up with a computer that is disconnected from the Internet and to buy the wallet directly from the device manufacturer to avoid being defrauded out of your money on device setup. This is not something you should buy used. In addition, your crypto is only as secure as your access to your cold wallet device.
Finally, since all cryptocurrency is stored on the blockchain, your cold wallet only holds your public and private keys. In order to transfer your funds from one cold storage wallet to another you still need to pay a transaction fee to update the blockchain with the new wallet address. It is theoretically possible to transfer funds from one cold wallet to another, but in order to do so you still need to access the blockchain network which can open the users up to security risks. This is why cold storage hardware wallets are used for storage and not for frequent transactions - the less contact the wallet has with the Internet, the safer it is.
These wallets are the equivalent of a bank account or bank vault. They are secure until their information is exposed and the fraudsters can rack up fraudulent transactions.
Type 4: Paper Wallets
A paper wallet is a type of cold storage that is a bit deprecated. These wallets are made by printing out a sheet of paper that contains your public and private keys in QR code format. This is best used as a temporary storage solution. Concerns with this method of wallet storage include printer errors that cause you to lose all of your money, hackers hacking into your printer buffers to get your private keys, and all of the other ways that paper can be damaged. The advantage that, if none of those things happen, your crypto is stored on paper, which is not a device that can be hacked into.Basically, these wallets are the crypto equivalent of cash. It is advised to store these papers in a secure safe or safe deposit box and import them into a cold storage hardware wallet at the soonest possible opportunity, in much the same way that you should not be hoarding cash under your mattress and instead deposit that cash into your bank account.
The Bottom Line
For most folks looking to make money online in the crypto space, a decentralized application wallet is probably the best choice. The amount of crypto earned from faucets, airdrops, and games is not really enough to pose a big concern. For those concerned about security, it may pay to have multiple decentralized application wallets that you use with each platform that you are interested in. You can discuss the safety of decentralized application wallets here.If you manage to gain a lot of crypto, investing in a cold storage wallet may be a good choice. Just keep in mind that every time you exchange your crypto from one wallet to another, you will pay transaction fees which vary based on the cryptocurrency that you're transferring in order to update the blockchain accordingly.
Last edited: